What is Elbow Stiffness?
Elbow stiffness typically occurs following surgery, an injury, or due to joint degeneration. An extended period of immobilization or damage to the elbow joint can cause the elbow’s soft tissues, ligaments, and tendons to stiffen. Pain and reduced range of motion may be associated with stiffness.
What Causes an Elbow to Stiffen?
The National Library of Medicine classifies elbow stiffness as traumatic or atraumatic; congenital or acquired. Trauma, burns, fractures, and pathologies of the nervous system are the most frequent causes, and the resulting rigidity is directly proportional to the severity of the injury; even elbow surgery done for trauma management can be complicated by post-operative rigidity.
How is a Stiff Elbow Diagnosed?
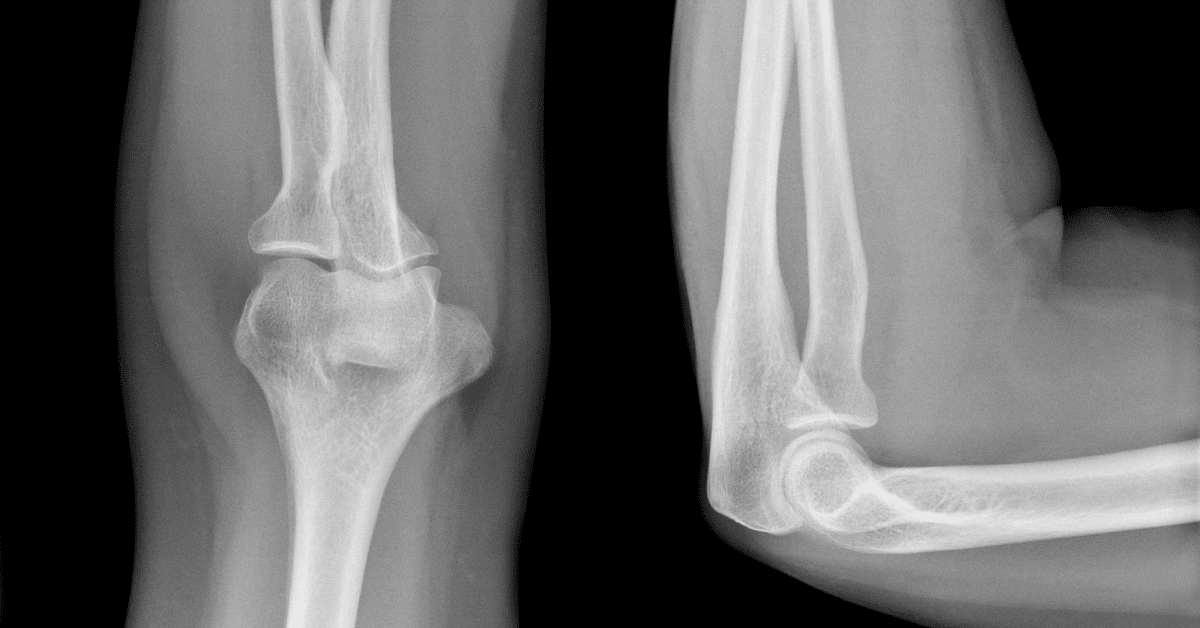
When diagnosing a patient's elbow stiffness, Dr. Donnelly will first perform a physical examination to determine the elbow's range of motion limitations. X-rays and CT scans may be performed to detect loose bodies or soft tissue abnormalities that could interfere with the elbow's movement. He will also discuss the patient’s lifestyle, review symptoms and previous injuries, and discuss treatments the patient has already tried.
Treatment Options
Non Surgical Treatment
Anti-inflammatory medications are used to treat inflammation and pain. Physical therapy is used to stretch and strengthen the ligaments, tendons, and muscles of the elbow. A splint may be used to limit movement of the elbow while the underlying condition heals.
Surgical Treatment
Open and endoscopic surgery options are available in cases which require surgery. Typically surgical cases are a result of a fracture, severe arthritis, or complications from a previous surgery.